Low-power spin detection in non-magnetic systems
A team of researchers from Université Grenoble Alpes - CNRS - Spintec, Unité Mixte de Physique CNRS-Thales, and Université d'Evry, and also including Dr. Diogo. C Vaz, currently at CIC nanoGUNE, reports on an alternative strategy to achieve low-power spin detection in a non-magnetic system. The results have now been published in Nature.
"After 50 years of development, the technology of today’s electronics is approaching its physical limits, with feature sizes smaller than 10 nanometres. It is also becoming clear that the ever-increasing power consumption of information and communication systems needs to be contained. These two factors require the introduction of non-traditional materials and state variables", state the authors in the paper.
As explained by Spintec, "Electron spin—a fundamentally quantum property—is central to spintronics, a technology that revolutionized data storage, and that could play a major role in creating new computer processors. In order to generate and detect spin currents, spintronics traditionally uses ferromagnetic materials whose magnetization switching consume high amounts of energy.
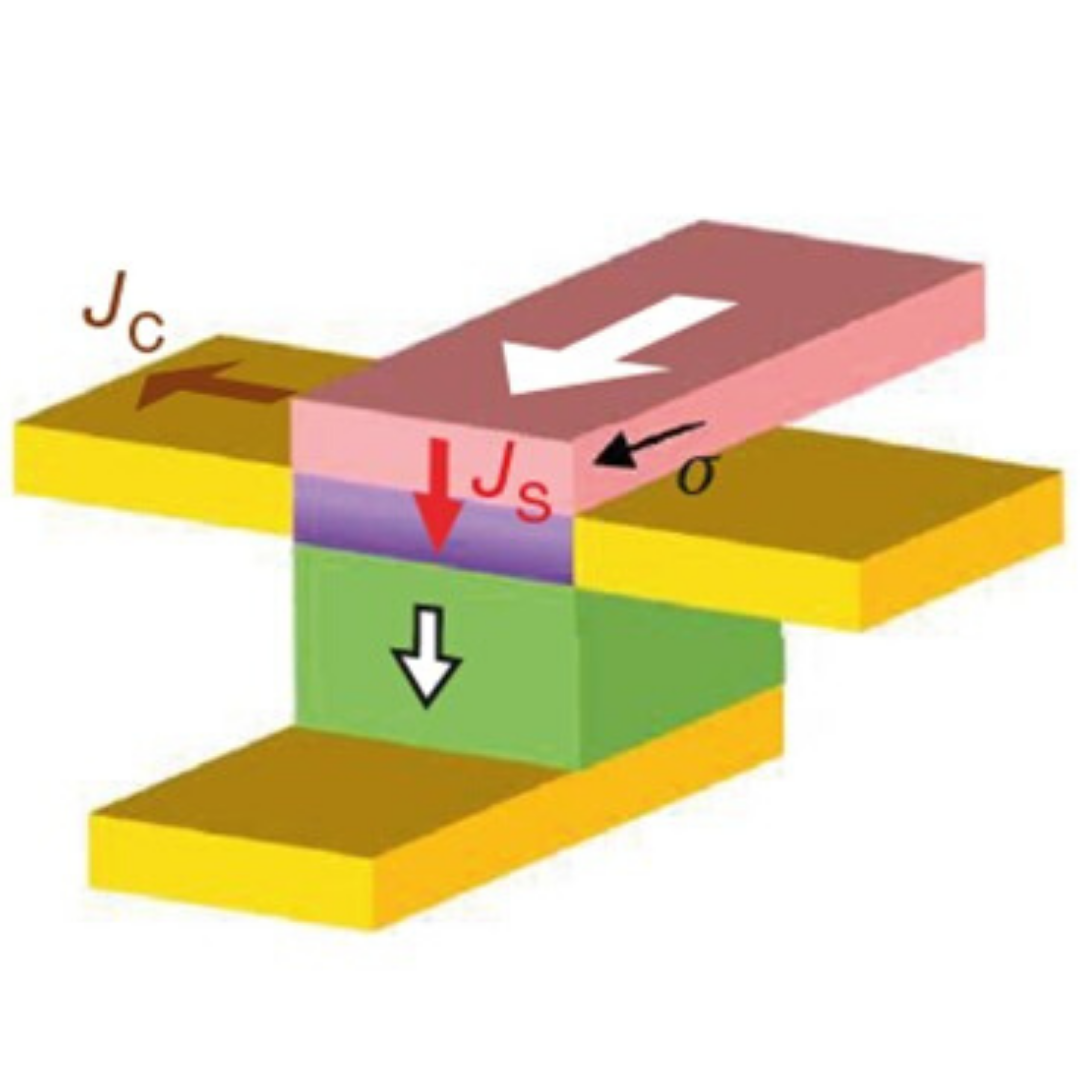
Diogo. C Vaz and co-workers demonstrate spin-to-charge conversion controlled by polarization reversal of a ferroelectric material. They harness the electric-field-induced ferroelectric-like state of strontium titanate (SrTiO3) to manipulate the spin–orbit properties of a two-dimensional electron gas, and efficiently convert spin currents into positive or negative charge currents, depending on the polarization direction.
"This research opens the way towards spintronic devices that operate on ferroelectricity rather than on ferromagnetism, thereby consuming 1,000 times less energy", conclude the Spintec team on their website.
Nature News and Views highlights that the method now reported is an example of low-power methods for controlling electrons spin, necessary to maintain the historic rates of progress that are occurring in computational power.
P. Noël, F. Trier, L. M. Vicente Arche, J. Bréhin, D. C. Vaz, V. Garcia, S. Fusil, A. Barthélémy, L. Vila, M. Bibes & J.-P. Attané.
Nature 580, 483-486 (2020)
Non-volatile electric control of spin-charge conversion in a SrTiO3 Rashba system
Nature News and view: Electric control of a spin current has potential for low-power computing, by Stefano Gariglio.
