PRL: Tuning the Magneto-Optical Response of Nanosize Ferromagnetic Ni Disks Using the Phase of Localized Plasmons
A team of researchers from different research centers and institutions, including nanoGUNE, has shown the physical mechanism underlying the ability to control the polarization of light exploiting the excitation of collective oscillations of conduction electrons in nanosize magnetic disks. The research was recently published in Physical Review Letters.
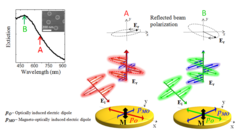
Metallic nanoparticles can interact strongly with light via collective oscillations of their conduction electrons, called localized plasmons. When light is shone onto a sample containing magnetic nanoparticles, the polarization of the reflected light slightly changes because of the “ordinary” magneto-optical (MO) activity arising from the quantum electron spin-orbit coupling in the constituent material. However, if also a localized plasmon is simultaneously excited, a “extraordinary” MO activity is observed, as reported by several studies to date.
A team of researchers carried out experiments on nickel nanodisks deposited on glass displaying localized plasmons and developed a simple physical model that unveils the physics underlying the appearence of such extraordinary plasmonic-related MO activity. The reported findings revealed a so far concealed pathway to tune the magnetic induced optical response of such meta-materials beyond what is offered by the intrinsic material properties through the excitation of localized plasmons. These effects might be exploited to make biological and chemical sensors with improved sensitivity or light modulators in nanophotonics.
Paolo Vavassori
Nanomagnetism Group
CIC nanoGUNE Consolider
Tolosa Hiribidea 76
E-20018 Donostia – San Sebastian
p.vavassori@nanogune.eu
www.nanogune.eu
