SMALL: Plasmonic Nickel Nanoantennas
In a recent article (J.Chen at al., Small, doi: 10.1002/smll.201100640) researchers from nanoGUNE have studied the fundamental optical properties of pure nickel nanoantennas. The article has been featured on the cover of the SMALL journal (Volume 7, Issue 16) and on the materials science news site Materials Views. “This study represents a step towards understanding and engineering magnetically controllable optical nanoantennas, which will be extremely useful for many developing technologies including biosensors, lasers, and solar cells”, says Richard Walters in his article “Nickel for Visible-Light Nanoantennas?”.
As explained in the abstract, the authors have studied the fundamental optical properties of pure nickel nanostructures by far-field extinction spectroscopy and optical near-field microscopy, providing direct experimental evidence of the existence of particle plasmon resonances predicted by theory. Experimental and calculated near-field maps allow for unambiguous identification of dipolar plasmon modes. By comparing calculated near-field and far-field spectra, they find dramatic shifts between the near-field and far-field plasmon resonance, which are much stronger than in gold nanoantennas. Based on a simple damped harmonic oscillator model to describe plasmonic resonances, it is possible to explain these shifts as due to plasmon damping.
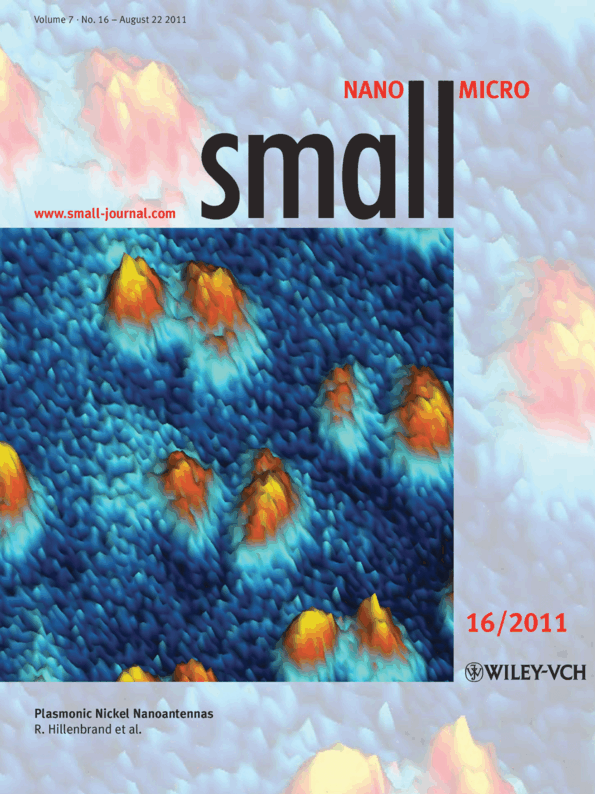
The cover shows the near-field amplitude image of dipolar plasmon modes in nickel nanodisks. Each disk exhibits two bright spots oscillating along the polarization direction of the incident light, revealing the enhanced near-field at the rims of the nickel disks. The image was recorded by a scattering-type scanning near-field microscope (s-SNOM) within a study of the optical and magnetic properties of nickel nanostructures. For more information, please read the Full Paper Plasmonic Nickel Nanoantennas
Rainer Hillenbrand Nanooptics Group
CIC nanoGUNE Consolider
Tolosa Hiribidea 76 200018 Donostia – San Sebastian, Spain
r.hillenbrand@nanogune.eu
www.nanogune.eu
